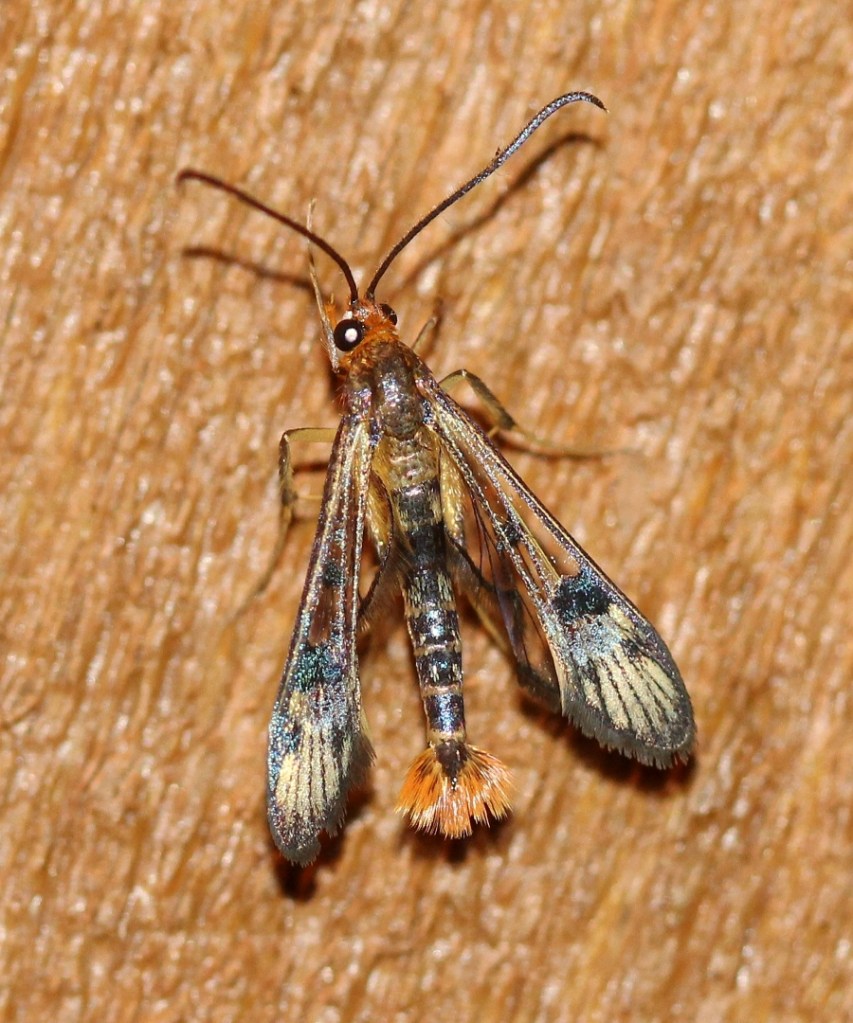
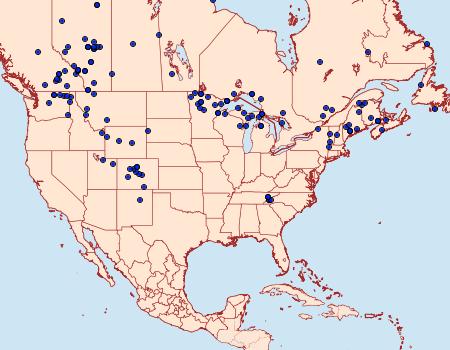
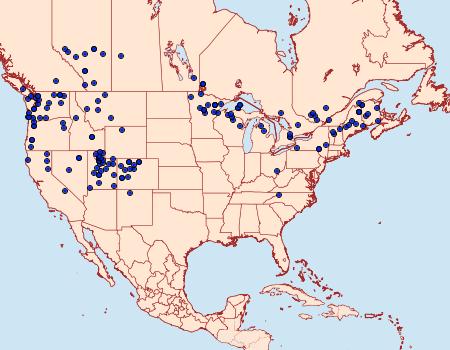
In a previous post, I wrote about syrphid flies that mimic bees and wasps. But are there other insects with this mimicry superpower? The answer is yes. Other types of flies, beetles, and moths all have species that mimic stinging insects. The moth Superfamily Cossoidea (Carpenter and Clearwing Moths) is notable for the many species that mimic stinging wasps.
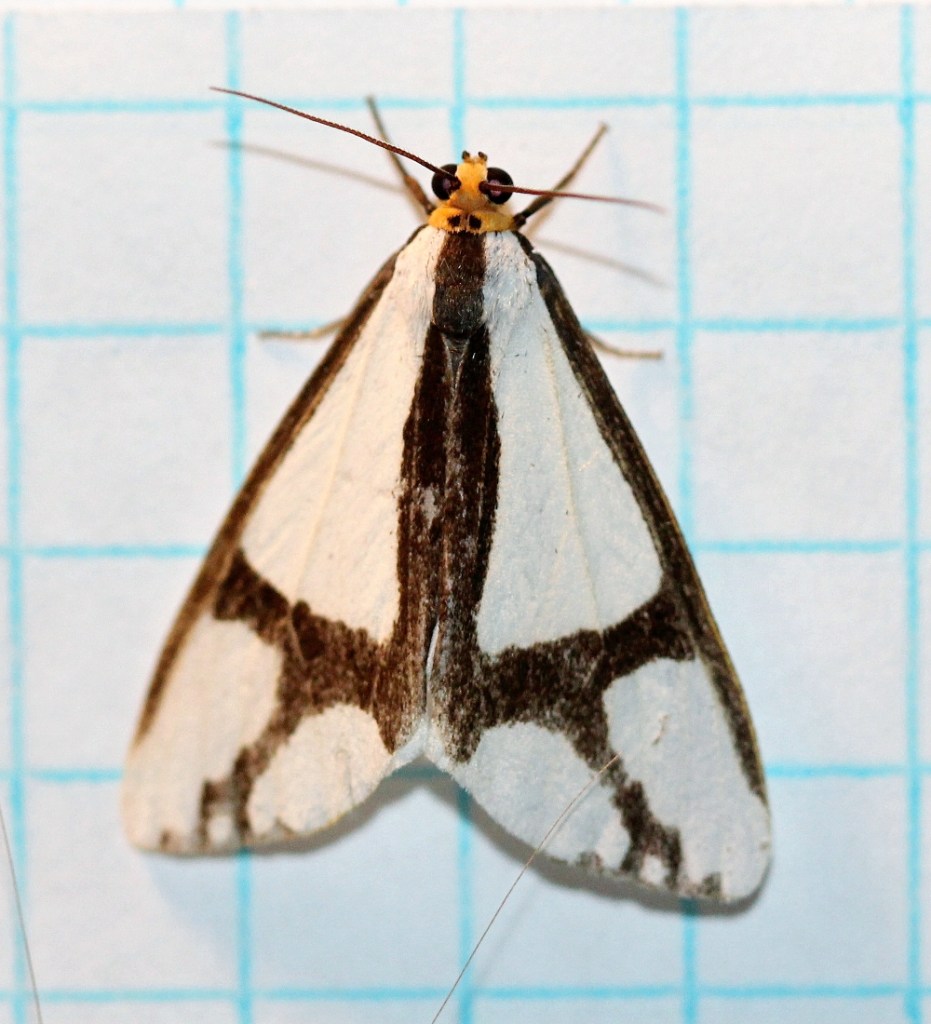
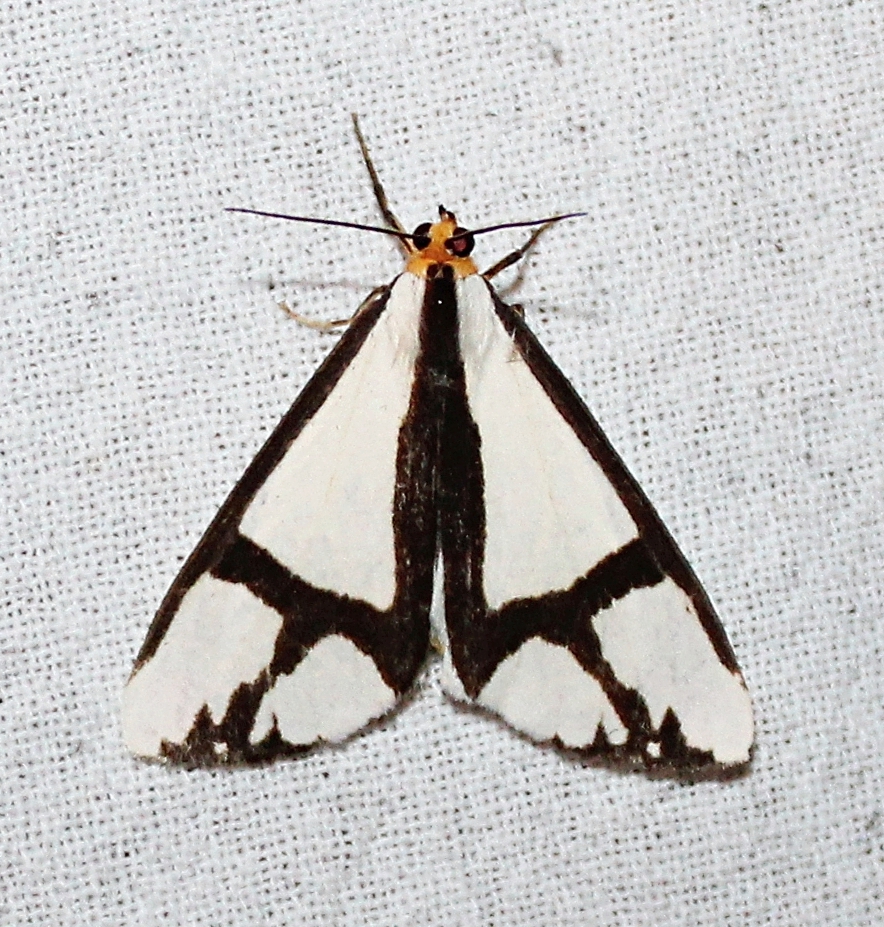
Synanthedon acerni (Family Sesiidae, Subfamily Sesiinae, Tribe Synanthedonini) is one such very wasp-like moth. Its wasp-like appearance allows it to be active during the day while it visits flowers, feeding on nectar.
Life history
The larvae of Synanthedon acerni are not quite as benign. Known as the maple callus borer moth, its larvae bore into the trunks of maple (Acer spp.) trees. Eggs are laid near wounds in the bark. Entry into the tree is through these wounds on the tree’s trunk. The larvae bore into the bark and then into the cambium, where they feed on the inner bark and sapwood. Feeding takes place during the summer within galleries. In the winter, they hibernate in the galleries and resume feeding in the spring.
At maturity, the larva constructs an oblong cocoon of wood fragments, frass, and silk within the gallery, close to the surface, covered by a thin escape window. When ready to emerge, the pupa cuts open the cocoon and the escape window. The fully formed Synanthedon acerni moth then exits the pupa, which is left partially stuck in the gallery.
The same tree may be used year after year, weakening it and eventually leading to its demise. A callus will form on the trunk after repeated infestations.